What Is Tendonitis And How Do You Treat It?
Category: Orthopedics
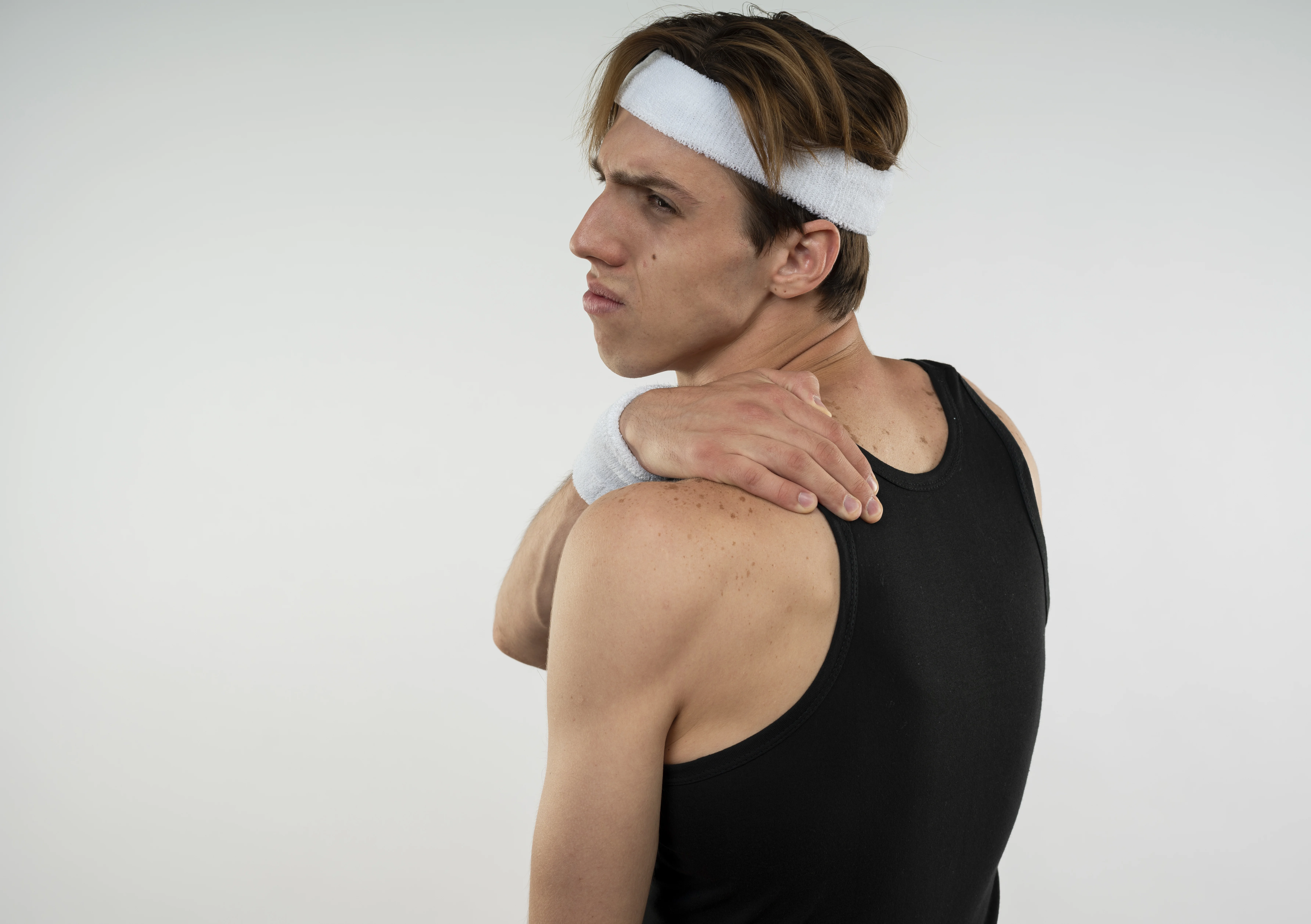
Tendonitis is the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, which is the thick, fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones. This condition is typically caused by overuse, repetitive motion, or sudden injuries and often results in pain, tenderness, and difficulty moving the affected area. While it can affect any tendon in the body, tendonitis is most commonly observed in the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and heels.
This condition can significantly impact daily life and physical activities, but with proper care and understanding of its causes, symptoms, and treatment strategies, recovery is achievable.
Understanding Tendonitis
Tendons are robust structures that help facilitate movement by transferring force from muscles to bones. However, they are not as flexible as muscles, making them prone to inflammation when subjected to excessive strain. Tendonitis is often named based on the affected area or associated activity, such as:
- Tennis Elbow: Tendonitis affecting the outer elbow.
- Golfer’s Elbow: Affecting the inner elbow.
- Jumper’s Knee: Inflammation of the patellar tendon in the knee.
- Achilles Tendonitis: Occurs in the Achilles tendon, located at the back of the ankle.
Symptoms of Tendonitis
The hallmark symptom of tendonitis is pain, which often worsens with movement. However, additional symptoms may vary based on the severity and location of the inflammation:
- Pain: Localized and sharp pain near the affected tendon, especially during movement.
- Tenderness: The area becomes sensitive to touch.
- Swelling: Inflammation can lead to noticeable swelling around the joint.
- Restricted Mobility: Movement becomes painful or limited due to stiffness in the tendon.
- Warmth and Redness: In some cases, the skin over the tendon may feel warm or appear red.
These symptoms can develop gradually or suddenly, depending on the cause of the condition.
Causes of Tendonitis
Tendonitis is primarily caused by repetitive motion or overuse of a tendon. However, several factors can increase the risk of developing this condition:
1. Repetitive Strain
Engaging in activities that involve repetitive movements, such as typing, painting, or certain sports, can overstrain the tendons.
2. Overuse or Improper Technique
Overloading tendons during exercise or using incorrect techniques can lead to inflammation. For instance, improper posture during weightlifting or running can strain tendons unnecessarily.
3. Age-Related Changes
As tendons lose elasticity with age, they become more susceptible to irritation and injury.
4. Sudden Injury
A sudden forceful impact, such as lifting something heavy without preparation, can cause micro-tears in the tendon.
5. Underlying Health Conditions
Certain conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes, can increase susceptibility to tendonitis by weakening or inflaming the tendons.
6. Occupational Hazards
Jobs requiring repetitive tasks or physical strain, such as construction, factory work, or even prolonged typing, can increase the risk of tendonitis.
Treatment Strategies for Tendonitis
Tendonitis can often be managed with a combination of self-care, medical treatment, and preventive measures. Addressing the condition early helps prevent complications and promotes faster recovery.
1. Self-Care and Home Remedies
- Rest: Giving the affected area time to heal by avoiding repetitive movements or heavy lifting is essential.
- Ice Therapy: Applying an ice pack to the area for 15–20 minutes several times daily reduces swelling and alleviates pain.
- Compression: Wrapping the affected area with an elastic bandage provides support and reduces swelling.
- Elevation: Keeping the injured area elevated above heart level minimizes inflammation.
2. Medications
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Topical Analgesics: Creams or gels applied to the skin can provide localized pain relief.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe pain, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to quickly reduce inflammation.
3. Physical Therapy
- Stretching Exercises: Gentle stretching increases flexibility and reduces stiffness in the tendon.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the surrounding muscles can relieve stress on the tendon and improve overall function.
- Ultrasound Therapy: Uses sound waves to promote tissue healing and reduce pain.
4. Advanced Medical Interventions
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting platelets from the patient’s blood into the affected tendon to stimulate healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, such as a tendon rupture, surgery may be necessary to repair the damage.
Preventing Tendonitis
Taking preventive measures is the best way to avoid tendonitis and its associated discomfort.
1. Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Always warm up before engaging in physical activity and cool down afterward. This prepares the tendons for movement and reduces strain.
2. Gradual Progression
Avoid sudden increases in the intensity or duration of physical activity. Gradual progression allows the body to adapt without overloading the tendons.
3. Ergonomic Adjustments
Incorporating ergonomic furniture and tools in your workspace can reduce strain on tendons during repetitive tasks.
4. Correct Technique
Using proper techniques in sports and physical activities minimizes unnecessary strain on tendons.
5. Strength and Flexibility Training
Incorporate exercises that strengthen muscles and improve tendon flexibility to support joint movements effectively.
6. Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration maintains tendon elasticity and prevents injuries.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Mild tendonitis often resolves with home care, but severe or persistent symptoms may require professional evaluation. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe pain or swelling that does not improve with rest.
- Difficulty moving the affected joint.
- Signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, and fever.
- Recurring episodes of tendonitis despite preventive efforts.
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospitals for Tendonitis Treatment?
Lokmanya Hospitals is trusted for tendonitis care, renowned for its expert medical team with extensive experience in treating musculoskeletal conditions. Equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic and therapeutic tools, the hospital offers advanced facilities to ensure accurate diagnoses and effective treatments. Patients benefit from customized treatment plans tailored to their unique needs and recovery goals, alongside a holistic approach that emphasizes both physical and emotional well-being. With Lokmanya Hospitals, you can feel confident in receiving comprehensive and effective care for tendonitis treatment and prevention.
Conclusion
Tendonitis is a common yet manageable condition that can significantly impact daily activities. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and following appropriate treatment strategies are key to recovery. By taking preventive measures and seeking professional care when needed, individuals can maintain healthy tendons and continue enjoying an active lifestyle.
If you suspect tendonitis or need guidance on managing joint pain, consult a healthcare provider promptly to ensure a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your needs.
FAQ’s
1. Can tendonitis heal on its own?
Mild cases of tendonitis may heal with rest and self-care measures, such as ice application and avoiding activities that aggravate the condition. However, persistent or severe cases often require medical intervention.
2. Is tendonitis the same as arthritis?
No, tendonitis is the inflammation of tendons, while arthritis refers to inflammation of the joints. They are distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments.
3. How long does it take to recover from tendonitis?
Recovery time varies based on the severity and location of the tendonitis. Mild cases may improve within a few weeks, while severe cases or those requiring surgery may take several months.
4. Are there any complications associated with untreated tendonitis?
Yes, untreated tendonitis can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, or tendon rupture, which may require surgical repair. Early treatment is essential to prevent these complications.
5. Can tendonitis affect children or teenagers?
Although tendonitis is more common in adults due to repetitive strain and age-related changes, it can also affect children and teenagers, especially those involved in repetitive sports or activities.
6. Can wearing the wrong footwear contribute to tendonitis?
Yes, improper footwear can strain tendons, particularly in the feet and ankles, increasing the risk of conditions like Achilles tendonitis or plantar fasciitis.