What Causes ADHD in the Brain?
Category: Neurology
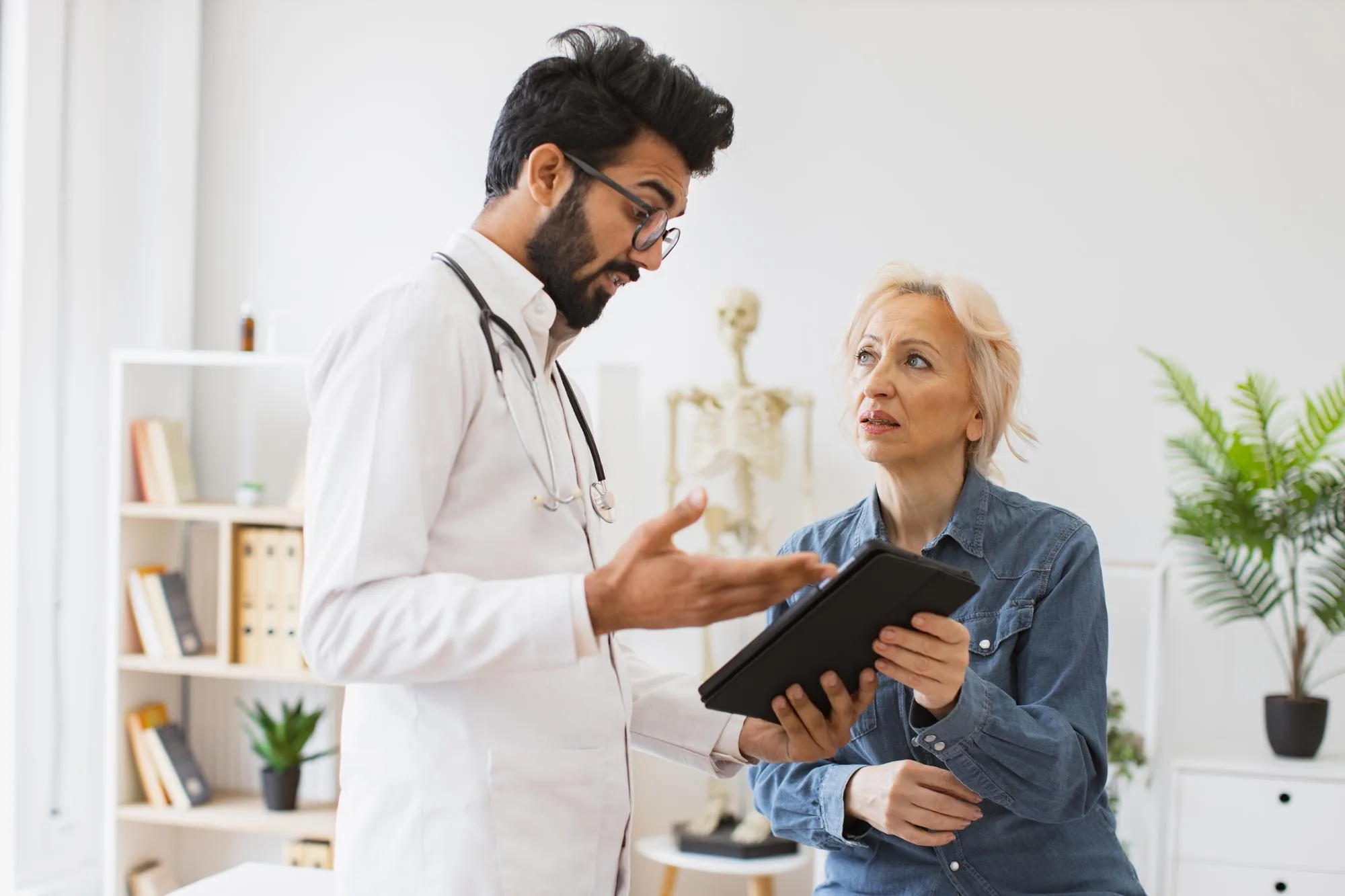
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurological condition that affects attention, impulse control, and behavior regulation. Understanding what causes ADHD in the brain is important for early identification and effective management. While genetics, brain structure, and neurotransmitter activity play a role, ADHD manifests differently in each individual, making personalized assessment crucial.
At Lokmanya Hospitals, our team of experienced ADHD doctors in Pune provides comprehensive evaluations to identify neurological patterns linked to ADHD. Through careful analysis of brain function, behavior, and cognitive performance, we design personalized therapy plans. With our evidence-based interventions, families can access structured ADHD treatment in Pune that addresses the root neurological factors and helps manage symptoms effectively.
How ADHD Develops in the Brain
ADHD is associated with differences in certain brain regions that control attention, executive functions, and emotional regulation. Research shows that both structural and functional variations contribute to the disorder.
Brain Structure Differences
- Prefrontal Cortex: This area, responsible for planning, focus, and impulse control, often shows underactivity or delayed maturation in individuals with ADHD.
- Basal Ganglia: Changes in this region affect motor control and the ability to regulate behavior, contributing to hyperactivity and restlessness.
- Cerebellum: This part of the brain plays a role in coordination and timing; differences here may influence attention and motor planning.
Neurotransmitter Activity
- Dopamine Dysregulation: Dopamine is critical for reward processing and motivation; imbalances can lead to difficulty sustaining focus and controlling impulses.
- Norepinephrine Imbalance: This neurotransmitter helps regulate attention and alertness; disruptions can affect concentration and responsiveness.
- Combined Effects: Interactions between neurotransmitter systems and structural differences create the neurological foundation for ADHD symptoms.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
ADHD is influenced by both hereditary and environmental elements.
- Genetics: Family history significantly increases the likelihood of ADHD, suggesting inherited brain function patterns play a role.
- Prenatal Environment: Exposure to toxins, maternal stress, or premature birth may affect neurological development and increase ADHD risk.
- Early Childhood Factors: Brain injuries, poor nutrition, or environmental stressors during early development can contribute to the emergence of ADHD symptoms.
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospitals for ADHD Care?
At Lokmanya Hospitals, we understand that ADHD originates from complex neurological factors that vary among individuals. Our team of ADHD doctors in Pune evaluates brain function, behavioral patterns, and cognitive performance to provide personalized care. By combining neurological insights with therapy and lifestyle guidance, we deliver evidence-based interventions that help manage symptoms effectively and improve daily functioning.
Conclusion
ADHD arises from a combination of brain structure differences, neurotransmitter imbalances, and genetic and environmental factors. While it cannot be fully cured, understanding these neurological causes helps guide treatment. At Lokmanya Hospitals, our experienced ADHD doctors in Pune provide personalized ADHD treatment in Pune to address these root factors, helping individuals manage attention, behavior, and emotional regulation. Families can trust Lokmanya Hospitals to deliver structured, comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s unique neurological profile.
FAQs
- What part of the brain causes ADHD?
ADHD is linked to the prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum, which regulate attention, behavior, and motor coordination. - Is ADHD purely genetic?
Genetics plays a significant role, but environmental factors like prenatal exposure and early childhood experiences also contribute. - What neurotransmitters are involved in ADHD?
Dopamine and norepinephrine are key neurotransmitters that influence focus, motivation, and impulse control. - Can brain differences in ADHD be detected?
Neurological assessments, imaging, and behavioral evaluations help identify patterns associated with ADHD. - Does ADHD get worse with age?
Symptoms can change over time; some adults learn coping strategies, but core neurological differences persist. - Can ADHD be prevented?
There is no guaranteed prevention, but early intervention and supportive environments can reduce severity of symptoms. - Why choose Lokmanya Hospitals for ADHD care?
We provide expert ADHD doctors in Pune, evidence-based therapies, and personalized plans targeting neurological causes for effective symptom management. - Are medications based on brain function?
Yes, medications target neurotransmitter imbalances to help improve focus and control impulses in ADHD.
Previous blog
 (1).webp)
Can ADHD Be Cured?
Next blog


 (1).webp)