Gout: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Strategies
Category: Blogs
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that occurs when uric acid builds up in the body and forms sharp crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and intense pain, swelling, and redness. It is often referred to as the "disease of kings" due to its historical association with rich foods and excessive alcohol consumption. However, gout can affect anyone, and it is important to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options to manage and prevent flare-ups effectively.
Symptoms Of Gout
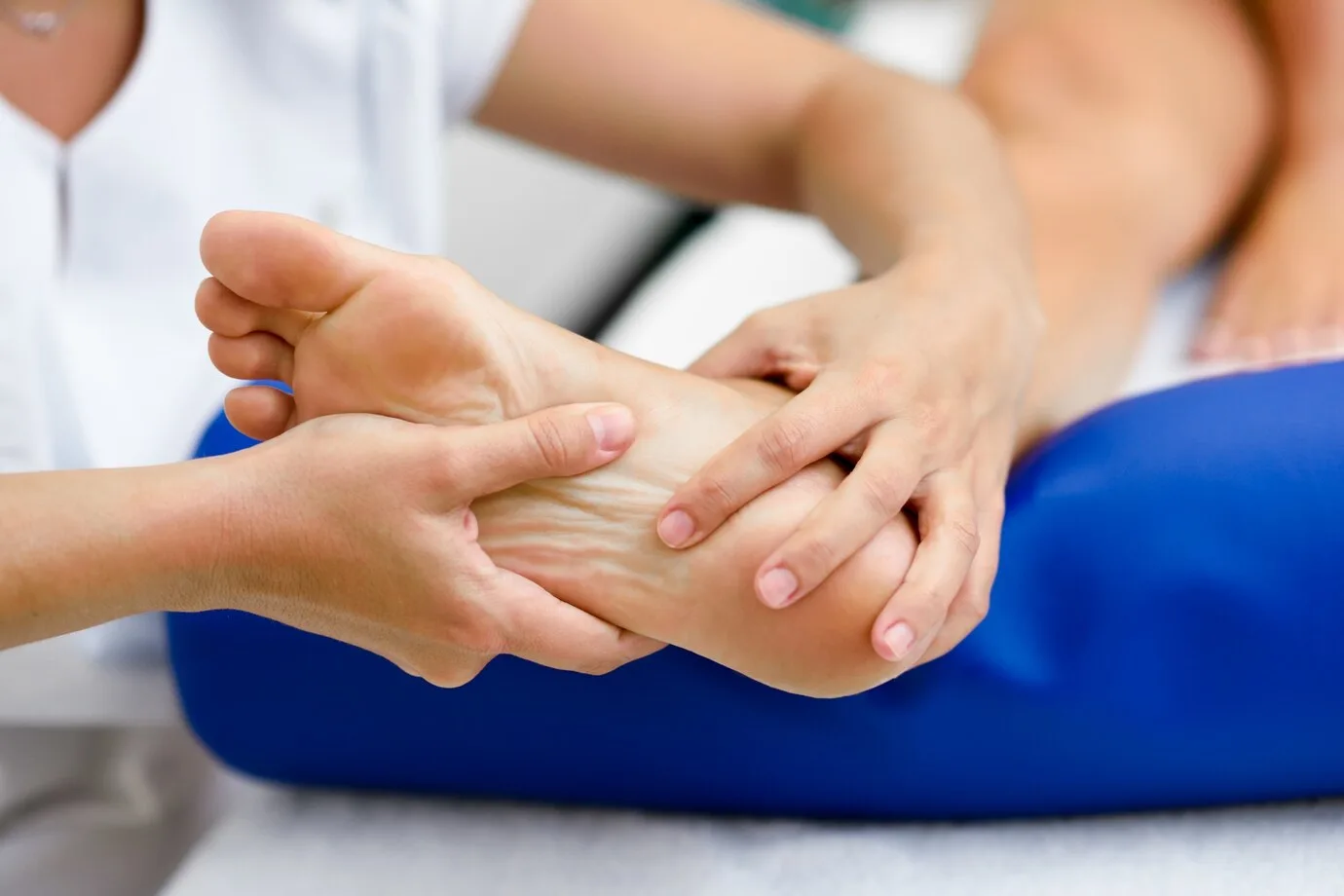
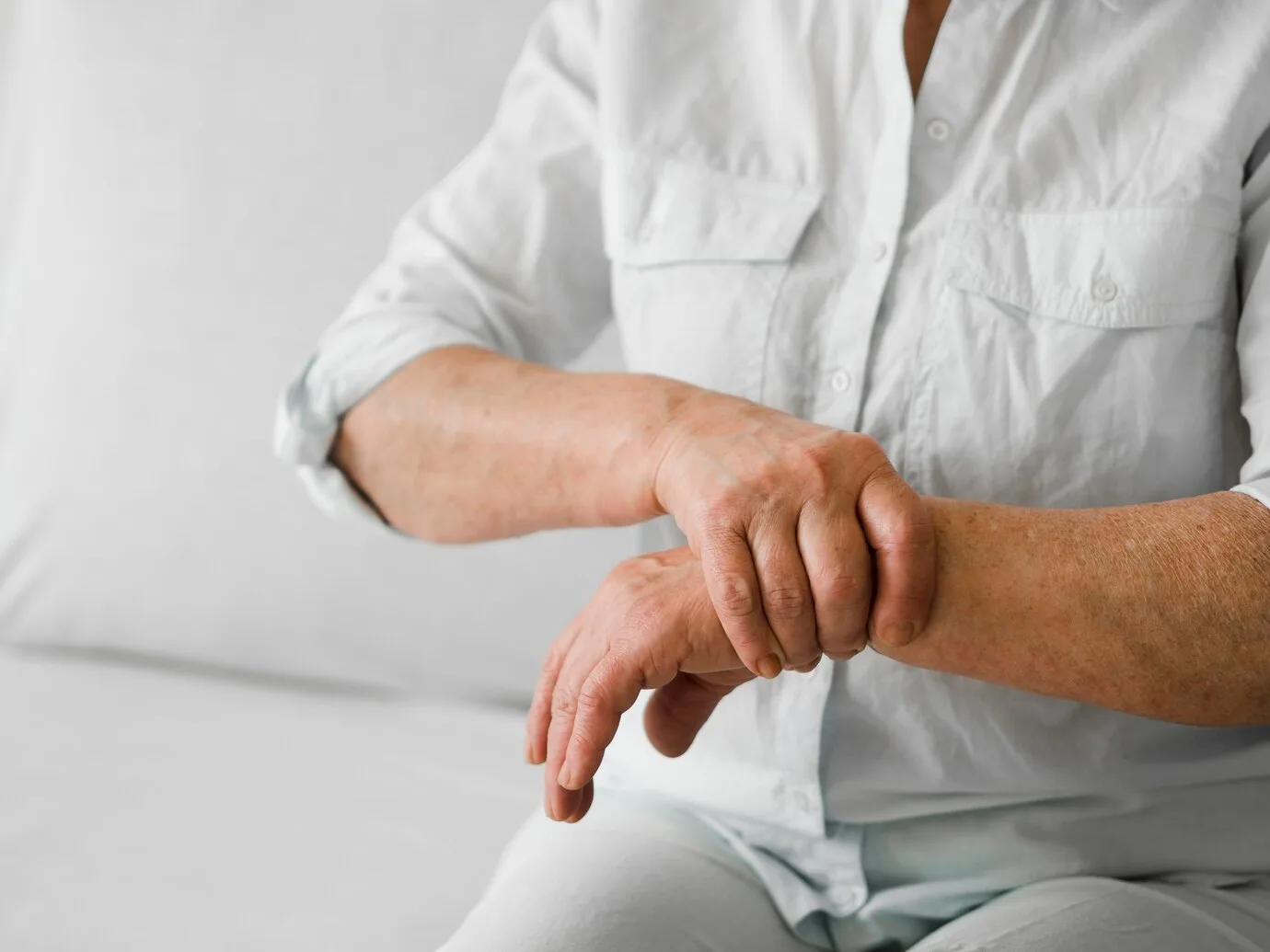
The most common symptom of gout is sudden, intense pain in the affected joint, typically occurring at night. The pain is often described as sharp, throbbing, or excruciating. Gout most commonly affects the big toe, but it can also involve other joints, such as the knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
Other common symptoms of gout include:
- Swelling: The affected joint becomes swollen and feels warm to the touch.
- Redness: The skin over the affected joint may appear red or purplish.
- Limited Mobility: The joint may become stiff, and movement can be very painful.
- Fever: In some cases, gout may cause a mild fever due to inflammation.
- Tophi: In long-term gout, uric acid crystals may form lumps under the skin, known as tophi, which are typically found around the joints, ears, or elbows.
Causes Of Gout
The primary cause of gout is the accumulation of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Uric acid is a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks, as well as in the body’s cells. Under normal circumstances, uric acid is excreted through urine. However, when the body produces too much uric acid or is unable to excrete it efficiently, it can accumulate and form crystals in the joints, leading to a gout attack.
Several factors can contribute to high levels of uric acid, including:
- Dietary Factors: Consuming foods rich in purines, such as red meat, shellfish, organ meats, and alcoholic beverages (especially beer), can increase uric acid production.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to higher levels of uric acid in the blood and decreased excretion.
- Genetics: A family history of gout can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease can impair the body’s ability to remove uric acid.
- Medications: Some medications, including diuretics, can increase uric acid levels.
Treatment Strategies For Gout
Effective treatment for gout focuses on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and preventing future attacks. The treatment plan may include a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments.
1. Medications
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): Medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation during a gout attack.
- Colchicine: This medication helps reduce inflammation and pain, especially when taken within the first 12 hours of a gout attack.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or injectable corticosteroids may be prescribed if NSAIDs or colchicine are ineffective or if the patient cannot tolerate them.
- Uric Acid-Lowering Medications: Drugs such as allopurinol and febuxostat help lower uric acid levels in the blood and prevent future gout attacks.
- Probenecid: This medication helps the kidneys excrete more uric acid, reducing its buildup in the body.
2. Dietary Changes
- Limit Purine-Rich Foods: Reducing the intake of foods high in purines, such as red meats, organ meats, shellfish, and alcohol (especially beer and spirits), can help lower uric acid levels.
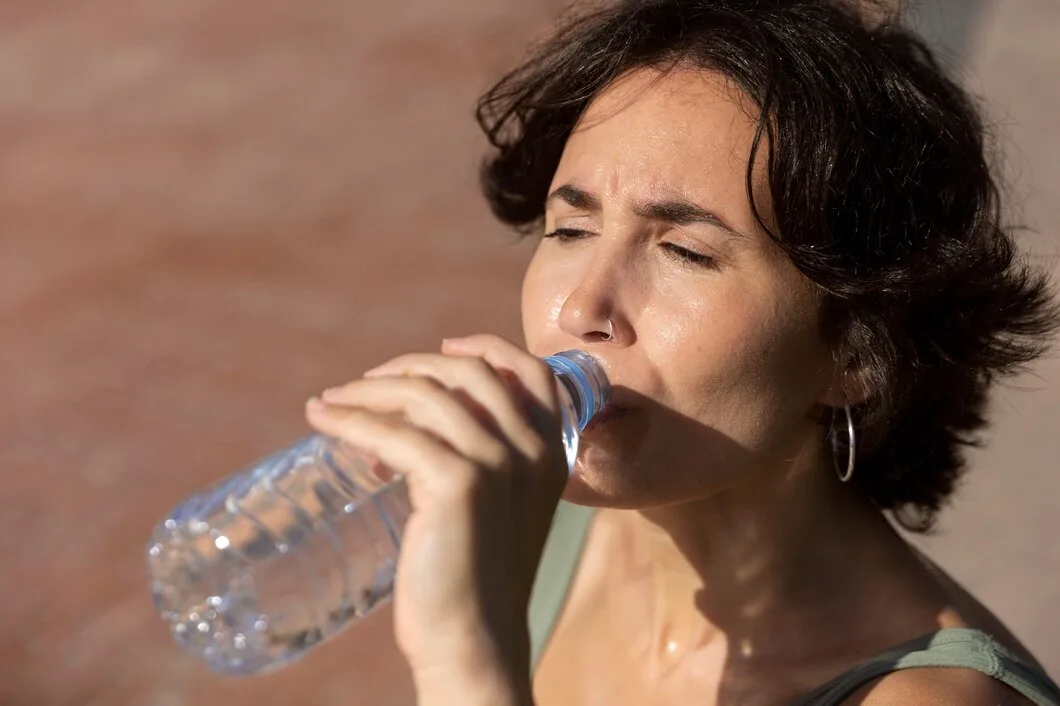
- Increase Water Intake: Staying hydrated helps the kidneys flush out uric acid more effectively. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day.
- Limit Sugary Drinks: Avoid sugary beverages, especially those containing high fructose corn syrup, as they can increase uric acid production.
- Eat Low-Fat Dairy and Vegetables: Low-fat dairy products and a variety of vegetables are recommended as part of a gout-friendly diet.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the production of uric acid and alleviate stress on the joints.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular, moderate exercise can help improve joint health and reduce the risk of gout flare-ups. However, avoid intense exercise during a gout attack.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Alcohol, particularly beer, and smoking can both increase the risk of gout attacks and interfere with treatment.
4. Preventing Future Gout Attacks
- Regular Monitoring of Uric Acid Levels: Working closely with your healthcare provider to monitor uric acid levels can help prevent future attacks and manage your condition more effectively.
- Long-Term Uric Acid-Lowering Treatment: In chronic cases, long-term medications to lower uric acid levels may be necessary to prevent recurrent gout attacks and reduce the risk of joint damage.
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospital For Gout Issues?
Lokmanya Hospitals is known for its expert medical team, state-of-the-art facilities, and patient-centered care. With a focus on delivering high-quality treatments at affordable prices, it ensures both your physical and emotional well-being. Offering personalized healthcare and a reputation for excellence, Lokmanya is a trusted choice for all your medical needs.
Conclusion
Gout is a painful and often debilitating condition, but with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes, it is manageable. If you experience symptoms of gout, such as sudden joint pain, swelling, and redness, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent further complications and improve your quality of life. By following a proper treatment plan and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, many individuals with gout can lead a healthy, active life without frequent flare-ups.
FAQs
1.Can gout be cured?
While there is no cure for gout, it can be effectively managed with medications and lifestyle changes. With proper treatment, gout flare-ups can be minimized or prevented.
2. How long does a gout attack last?
A gout attack typically lasts between 3 to 10 days, with the most intense pain occurring in the first 24 to 36 hours. Prompt treatment can shorten the duration and severity of the attack.
3. Is gout hereditary?
Yes, gout can be hereditary. If you have a family history of gout, you may be more likely to develop the condition yourself.
4. Can gout affect other joints besides the big toe?
Yes, while gout most commonly affects the big toe, it can also affect other joints, including the knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
5. Can I exercise if I have gout?
During a gout attack, it is advisable to rest the affected joint. However, regular, low-impact exercises like walking or swimming can help manage weight and improve joint health to reduce the risk of future flare-ups.