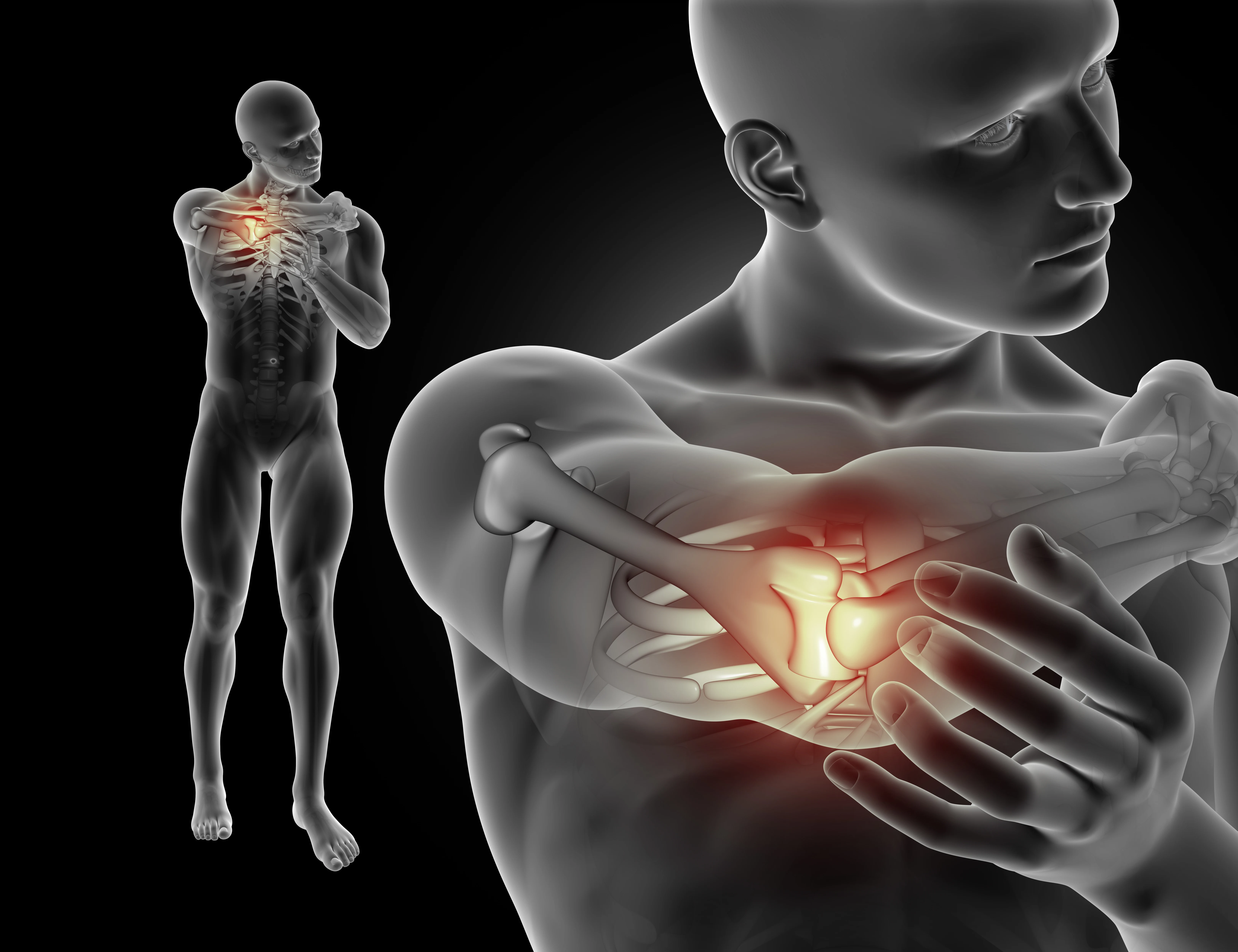
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Causes And Treatments
Category: Blogs
The carpal tunnel is a small space in the wrist formed by bones and ligaments. It houses the median nerve, which controls sensations in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger. It also powers the muscles at the base of the thumb. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome occurs when this tunnel becomes compressed or inflamed, putting pressure on the median nerve and disrupting its function.
Symptoms Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
CTS symptoms often develop gradually and may worsen over time if left untreated. Common signs include:
- Numbness and Tingling: Often felt in the thumb, index, and middle fingers, especially at night.
- Pain: Sharp or burning pain that may extend from the wrist up to the arm or shoulder.
- Weakness: Difficulty gripping objects or performing precise tasks like buttoning a shirt.
- Swelling Sensation: A feeling of puffiness in the fingers, even if no visible swelling is present.
- Hand and Wrist Stiffness: Particularly noticeable in the morning.
If symptoms persist, they may progress to permanent nerve damage, emphasizing the need for early intervention.
Causes Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
CTS has multiple contributing factors, ranging from repetitive hand movements to medical conditions. Some of the key causes include:
1. Repetitive Hand and Wrist Movements
- Tasks like typing, assembly line work, or using vibrating tools can strain the wrist, leading to swelling and nerve compression.
2. Wrist Anatomy
- A naturally smaller carpal tunnel, due to genetics or bone structure, increases the likelihood of developing CTS.
3. Underlying Medical Conditions
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes joint inflammation that can narrow the carpal tunnel.
- Diabetes: Leads to nerve damage, making the median nerve more susceptible.
- Thyroid Disorders: Fluid retention associated with hypothyroidism can increase pressure on the median nerve.
4. Hormonal Changes
- Pregnancy and menopause often cause fluid retention and swelling, heightening the risk of CTS.
5. Wrist Injuries
- Fractures, sprains, or trauma can alter the space in the carpal tunnel, leading to compression of the nerve.
6. Workplace Factors
- Jobs that involve repetitive wrist movements or prolonged use of vibrating equipment increase the risk of CTS.
Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Diagnosing CTS involves a combination of physical examinations and diagnostic tests:
1. Physical Examination
- Doctors may perform tests like the Tinel’s sign or Phalen’s test to identify nerve compression.
2. Nerve Conduction Studies
- These measure how quickly electrical signals travel through the median nerve to determine the extent of nerve damage.
3. Imaging Tests
- X-rays or ultrasounds may be used to rule out other conditions, such as arthritis or fractures.
Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment for CTS aims to relieve symptoms, improve hand function, and prevent further nerve damage. Options range from conservative approaches to surgical interventions.
Non-Surgical Treatments
1. Wrist Splints
Wearing a splint, especially at night, keeps the wrist in a neutral position and reduces pressure on the median nerve.
2. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen help manage inflammation and pain.
Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief by reducing swelling in the carpal tunnel.
3. Activity Modifications
Adjusting workplace ergonomics and taking regular breaks during repetitive tasks can alleviate strain on the wrist.
4. Physical Therapy
Stretching and strengthening exercises for the wrist and hand can improve flexibility and reduce symptoms.
Surgical Treatments
For severe or persistent cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
1. Open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- The surgeon makes an incision in the palm to cut the ligament and enlarge the carpal tunnel.
2. Endoscopic Surgery
- A less invasive procedure using a small camera to guide the release of the ligament through tiny incisions.
Both procedures are highly effective in relieving symptoms and improving hand function, with most patients experiencing significant improvement within weeks.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
While CTS is not always preventable, taking steps to reduce stress on the wrists can lower the risk of developing the condition:
- Practice Good Ergonomics: Keep wrists in a neutral position and use ergonomic tools like keyboards and mouse pads.
- Take Frequent Breaks: Incorporate short breaks to stretch and rest your hands during repetitive activities.
- Strengthen Hand Muscles: Engage in exercises that build wrist and hand strength to support joint health.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Properly address conditions like diabetes or arthritis that can contribute to CTS.
When To Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent numbness, tingling, or weakness in your hand, consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent long-term complications and restore normal hand function.
Living With Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
With proper management, most people with CTS can lead a normal, active life. Incorporating preventive measures, adhering to treatment plans, and making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospital For CTS?
Lokmanya Hospital is a trusted destination for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) treatment, offering a comprehensive approach led by an expert team of orthopedic specialists, neurologists, and hand surgeons. Equipped with advanced diagnostic tools, our team ensures precise identification of CTS and provides tailored treatments, from non-surgical options like splints and therapy to minimally invasive surgical techniques for faster recovery. With a focus on patient comfort, clear communication, and dedicated rehabilitation programs, Lokmanya Hospital delivers compassionate care to help patients regain hand strength and function effectively.
Conclusion
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a manageable condition when diagnosed early and treated effectively. By understanding its causes and symptoms, taking preventive measures, and seeking timely medical care, you can minimize its impact on your daily life. Whether through non-surgical methods or surgical intervention, relief is attainable, allowing you to regain comfort and mobility.
If you're experiencing symptoms of CTS, don’t delay consulting a healthcare professional to explore your options for treatment and long-term relief.
FAQ’s
1. Can carpal tunnel syndrome affect both hands at the same time?
Yes, carpal tunnel syndrome can affect both hands, although symptoms may vary in severity between the hands.
2. How long does recovery take after surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Recovery typically takes a few weeks to months, depending on the severity of the condition and the surgical approach used.
3. Are there any specific exercises that can help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome?
Yes, exercises that strengthen and stretch the wrist, hand, and forearm muscles can help reduce the risk of CTS.
4. Can untreated carpal tunnel syndrome lead to permanent nerve damage?
If left untreated, CTS can cause permanent damage to the median nerve, leading to loss of sensation and muscle weakness.
5. Is carpal tunnel syndrome hereditary?
While CTS itself is not hereditary, genetic factors influencing wrist anatomy or other related conditions may increase the risk.