What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Category: Blogs
Type 2 diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide, affecting millions and leading to serious complications if not managed properly. It is one of the most common forms of diabetes, and understanding what is Type 2 diabetes?, its causes, symptoms, and treatments can empower you to take charge of your health.
At Lokmanya Hospitals, known as the best hospital for diabetes treatment in Pune, we offer advanced care and personalized management plans for Type 2 diabetes. Our multidisciplinary team uses the latest diagnostic tools and treatment protocols to ensure every patient receives comprehensive, compassionate care.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels caused primarily by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the body produces little or no insulin, Type 2 diabetes involves the body’s ineffective use of insulin, a hormone essential for regulating blood glucose.
- What is insulin resistance?
It means that the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin, causing glucose to accumulate in the bloodstream. - Why does this happen?
Several factors like genetics, lifestyle, and obesity contribute to insulin resistance.
How Does Type 2 Diabetes Develop?
In the early stages, the pancreas compensates for insulin resistance by producing more insulin. However, over time, it cannot keep up with the demand, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This chronic high glucose state damages blood vessels and organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Common Causes and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes
1. Genetics and Family History
- Why does family history matter?
If close relatives have Type 2 diabetes, your risk is significantly higher, suggesting genetic predisposition.
2. Overweight and Obesity
- Excess fat, especially around the abdomen, produces hormones and inflammatory substances that interfere with insulin action.
3. Sedentary Lifestyle
- Lack of physical activity reduces the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
4. Unhealthy Diet
- Diets high in processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats contribute to insulin resistance.
5. Age
- Risk increases significantly after age 45 due to metabolic and hormonal changes.
6. Other Conditions
- Conditions such as hypertension, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and certain hormonal disorders also increase risk.
What Are the Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes?
Often developing gradually, Type 2 diabetes symptoms can be subtle or absent in early stages. Common signs include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds or infections
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
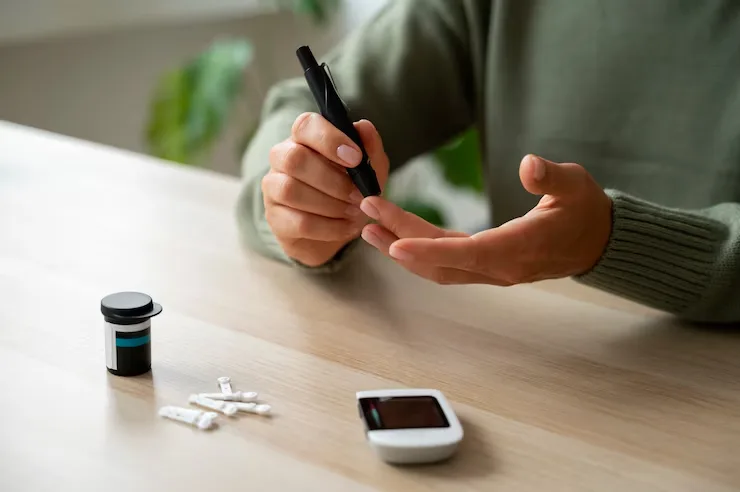
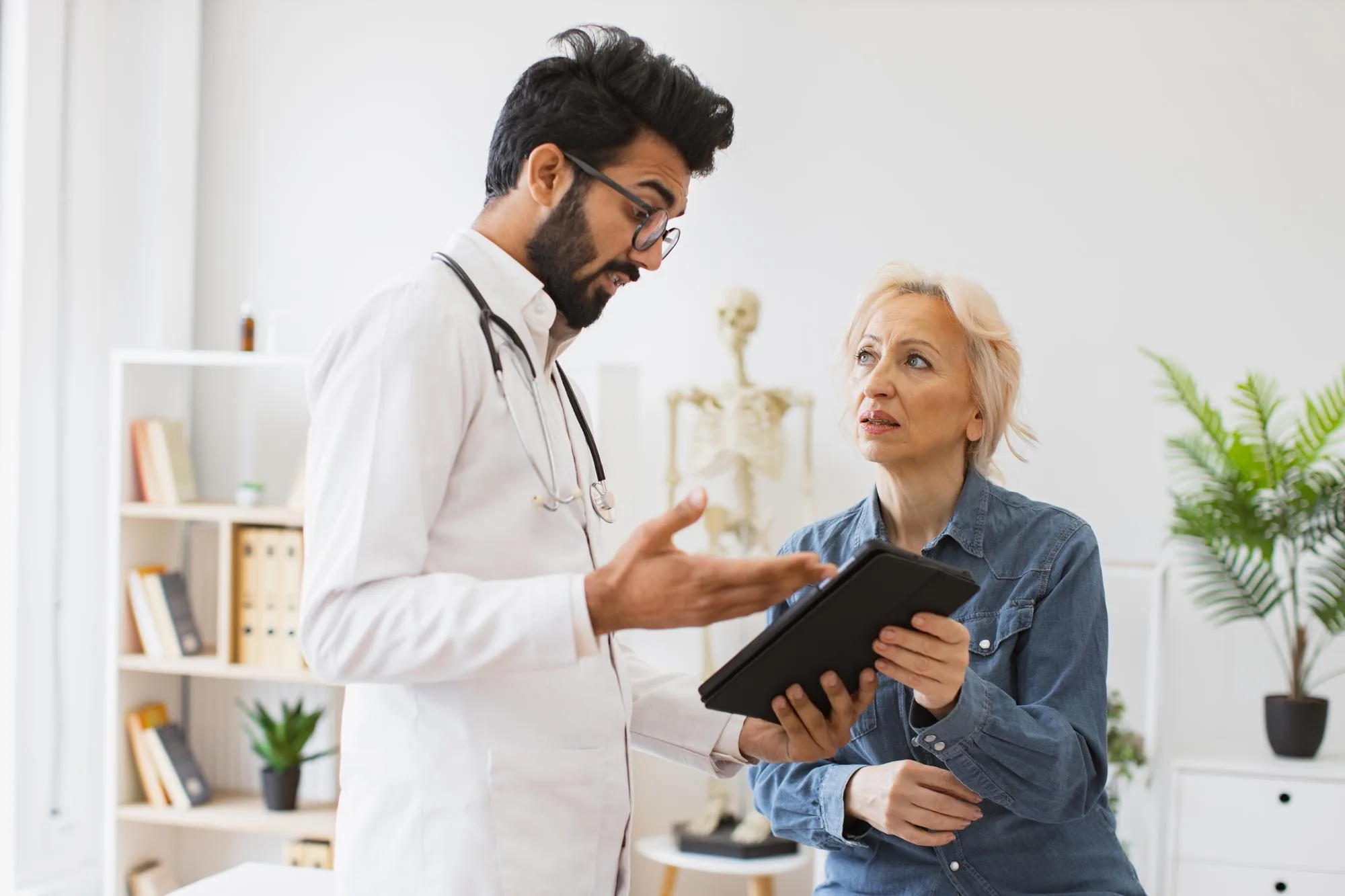
When Should You Get Tested for Type 2 Diabetes?
If you experience symptoms or have risk factors like family history or obesity, consult your healthcare provider for screening. Blood tests such as fasting glucose, HbA1c, or oral glucose tolerance test help diagnose diabetes.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Treated?
Effective management combines lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy, balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables
- Regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity
- Weight loss to reduce risk and manage blood sugar levels
Medications
- Oral hypoglycemics that help lower blood sugar
- Insulin therapy in advanced cases
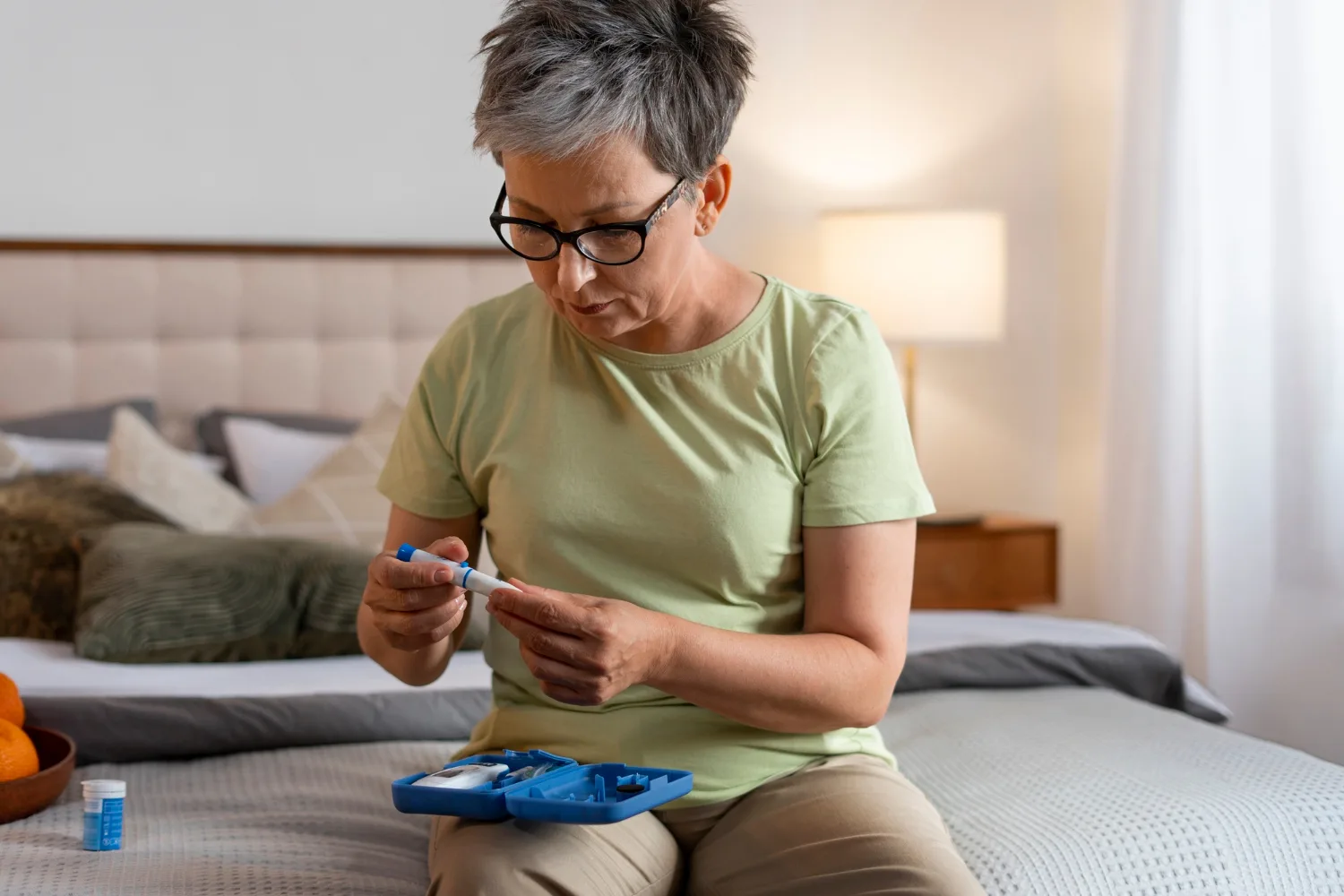
Monitoring
- Regular blood sugar monitoring to keep levels within target range
- Routine check-ups for complications
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes: What You Can Do
Preventing Type 2 diabetes starts with lifestyle:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a balanced, nutritious diet
- Stay physically active dail
- Avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol
- Manage stress effectively
- Regularly monitor blood sugar if at risk
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospitals for Type 2 Diabetes Care?
Lokmanya Hospitals is recognized as the best hospital for diabetes treatment in Pune due to its patient-centric approach and use of cutting-edge technology. Our team of expert endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators work collaboratively to design personalized treatment plans that fit your lifestyle and health goals.
We emphasize not just treating diabetes but preventing its complications. With advanced diagnostics, minimally invasive procedures, and continuous patient education, Lokmanya Hospitals ensures you get the best possible care. Thousands of satisfied patients trust us for our expertise, compassion, and excellent outcomes.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a manageable but serious condition that requires timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and sustained lifestyle changes. If you or your loved ones are at risk or living with Type 2 diabetes, consulting experts at Lokmanya Hospitals — the best hospital for diabetes care in Pune — can help you lead a healthy, active life. Our comprehensive approach ensures that you receive personalized care aimed at controlling blood sugar and preventing complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why does Type 2 diabetes develop?
It develops due to insulin resistance combined with decreased insulin production over time, influenced by genetics and lifestyle. - What lifestyle changes help manage Type 2 diabetes?
Healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management, and stress reduction are key. - When should medication be started?
When lifestyle changes are insufficient to maintain blood sugar levels within the target range. - Can Type 2 diabetes be reversed?
With significant lifestyle changes, some people can achieve remission, but ongoing management is essential. - What are the complications if Type 2 diabetes is not controlled?
Heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, eye problems, and increased infection risk.
Previous blog
How To Reduce High Blood Pressure?
Next blog