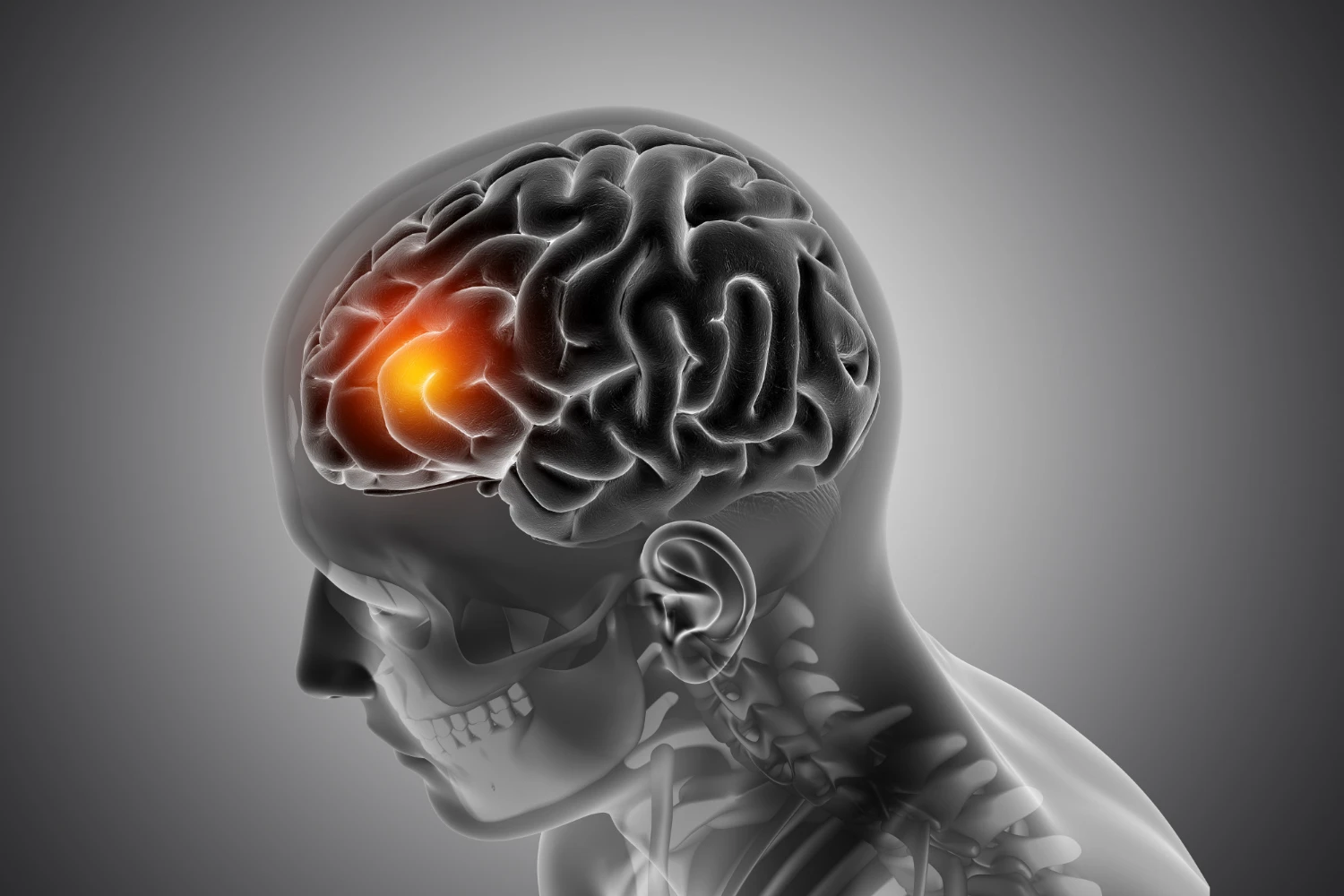
What Is Brain Tumor?
Category: Neurology
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within or around the brain. It can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), with some tumors growing silently over years and others progressing rapidly with life-threatening consequences. Because the brain governs essential bodily functions, even a small tumor in a sensitive area can lead to serious complications. Understanding what brain tumors are, why they occur, and how they are detected and treated is crucial for timely care and better outcomes.
In this blog, we’ll explore the symptoms and causes of diagnosis and treatment options. You’ll also learn why choosing a trusted name like Lokmanya Hospitals, known as one of the best neurology hospitals in Pune, can make all the difference in managing such critical conditions. With expert neurosurgeons, state-of-the-art imaging, and advanced neurological care, Lokmanya offers holistic, patient-centered treatment for brain tumor cases.
What Is a Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in your brain. Some tumors are primary, meaning they originate in the brain. Others are secondary (metastatic), which means they spread from other parts of the body (like the lungs or breasts).
Brain tumors are classified into:
Benign Brain Tumors
Benign brain tumors are non-cancerous growths that develop slowly and typically do not spread to other parts of the brain or body. Because they grow at a gradual pace, symptoms may appear slowly or sometimes not at all for years. These tumors usually remain confined to one area, making them easier to treat surgically.
Despite being non-cancerous, benign tumors can still cause serious problems depending on their size and location. Since the skull limits space, even a slow-growing tumor can increase pressure on the brain, affecting vital functions like movement, vision, or speech. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications.
Malignant Brain Tumors
Malignant brain tumors are cancerous and grow rapidly, often invading and destroying nearby healthy brain tissue. Their aggressive nature means symptoms can develop suddenly or worsen quickly, causing severe neurological issues. These tumors are more challenging to treat because they infiltrate surrounding areas, making complete surgical removal difficult.
Due to their fast growth and tendency to spread within the brain, malignant tumors require aggressive treatment, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Even with treatment, there is a higher risk of recurrence, so ongoing monitoring and care are critical for managing the disease and improving survival chances.
Types of Brain Tumors
Brain tumors are broadly categorized based on the type of cells they originate from:
1. Gliomas
- These arise from glial cells, which support brain function.
- Types include astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and glioblastomas.
- Glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most aggressive forms.
2. Meningiomas
- Develop in the meninges, the protective layers of the brain and spinal cord.
- Usually benign, but location can cause complications.
3. Pituitary Adenomas
- Affect the pituitary gland; often benign but can impact hormonal balance.
4. Medulloblastomas
- Common in children.
- Fast-growing and often located at the base of the skull.
5. Metastatic Tumors
- Originating from cancers in other body parts.
- Common in advanced cancer patients.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of most brain tumors is unknown, but several risk factors include:
- Genetic mutations and family history
Changes or mutations in certain genes can trigger abnormal cell growth in the brain. A family history of brain tumors may increase an individual’s risk due to inherited genetic factors. - Radiation exposure
Exposure to high doses of radiation, either from medical treatments or environmental sources, can damage brain cells and increase the likelihood of tumor development. This risk is higher in people who have undergone radiation therapy to the head. - Age
Brain tumors can occur at any age but are more commonly diagnosed in children and older adults. This is because certain tumor types are prevalent at these stages due to developmental or aging-related factors. - Immune suppression or underlying health issues
Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive medications, reduce the body’s ability to detect and destroy abnormal cells. This increases vulnerability to tumors, including those in the brain.
While not all tumors can be prevented, early detection can make a significant difference.
Symptoms of Brain Tumors
The symptoms of a brain tumor depend on its size, location, and rate of growth. Some of the first signs may include:
- Persistent headaches, often worse in the morning
Brain tumors can cause increased pressure inside the skull, leading to headaches that are frequently more intense in the morning. These headaches may not respond well to usual painkillers. - Seizures
Tumors can disrupt normal brain activity, causing sudden and uncontrolled electrical disturbances known as seizures. Seizures may affect movement, sensation, or consciousness. - Nausea and vomiting
Increased pressure on the brain or involvement of areas controlling nausea can cause frequent vomiting, often unrelated to food intake. This is a common symptom in brain tumor patients. - Vision or speech difficulties
Tumors near areas responsible for vision or speech can lead to blurred vision, double vision, or trouble speaking clearly. These symptoms vary based on the tumor’s location. - Cognitive changes, memory loss, or confusion
Tumors can impair brain functions, resulting in difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, or disorientation. These changes can affect daily tasks and decision-making. - Loss of balance or coordination
If a tumor affects the cerebellum or related pathways, it can cause problems with walking, balance, and hand-eye coordination. This may lead to frequent falls or clumsiness. - Weakness or numbness in limbs
Tumors pressing on motor areas can cause weakness, tingling, or numbness in arms or legs. This may be gradual or sudden, affecting one or both sides of the body. - Mood or personality changes
Brain tumors can alter the areas that regulate emotions and behavior, leading to noticeable mood swings, irritability, or personality shifts. These changes can affect relationships and social interactions.
If you experience these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a neurologist for further evaluation.
When to See a Neurologist?
If your symptoms persist for more than a few days or worsen, you should see a neurologist immediately. Delays in diagnosis can lead to complications, especially for fast-growing brain tumors.
Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
Diagnosing a brain tumor involves several steps:
1. Neurological Exam
- Your doctor will evaluate balance, reflexes, vision, and coordination.
2. Imaging Tests
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is the most effective method for brain tumor detection.
- CT scans can help detect bleeding or large masses.
3. Biopsy
- If a tumor is detected, a biopsy may be performed to determine its type and whether it's cancerous.
Brain Tumor Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor. Here are the most common options:
1. Surgery
- The first-line treatment for most brain tumors.
- Aim is to remove as much tumor as possible without damaging vital brain tissue.
2. Radiation Therapy
- Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Often used when surgery is not possible.
3. Chemotherapy
- Involves drug-based treatment to kill or slow tumor growth.
- Can be taken orally or intravenously.
4. Targeted Therapy
- Focuses on specific abnormalities in tumor cells.
5. Rehabilitation
- Post-treatment support includes physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy to improve quality of life.
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospitals for Brain Tumor Treatment?
Lokmanya Hospitals is recognized as one of the best neurology hospitals in Pune, offering comprehensive brain tumor care. With expert neurologists, advanced imaging equipment, and state-of-the-art operating theaters, Lokmanya ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment—whether it's a benign tumor or a high-grade malignancy.
What sets Lokmanya apart is its multidisciplinary team of neurosurgeons, neuro-oncologists, radiologists, and rehabilitation specialists who work together to create personalized treatment plans. Their minimally invasive surgical techniques, post-op care, and patient-first philosophy make them a preferred choice for brain tumor treatment in India.
Final Thoughts
Brain tumors can be overwhelming, but with the right medical care, patients can lead fulfilling lives. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is the first step towards timely intervention. If you or a loved one are facing signs of a neurological condition, trust only the best neurology doctors in Pune—Lokmanya Hospitals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the first sign of a brain tumor?
A persistent headache, especially one that worsens in the morning or with physical activity, is often the first symptom. Accompanying issues like nausea, blurred vision, or confusion may also occur.
Q2. Are brain tumors curable?
Some benign brain tumors can be completely removed through surgery. Malignant tumors can often be managed with a combination of treatments, improving life expectancy and quality of life.
Q3. How quickly do brain tumors grow?
The growth rate depends on the type. Glioblastomas, for instance, are aggressive, while meningiomas may grow slowly over years.
Q4. What is the survival rate for brain tumors?
Survival rates vary widely based on tumor type, location, patient age, and treatment. Early diagnosis significantly improves outcomes.
Q5. Is brain tumor treatment painful?
With advanced surgical techniques and anesthesia, brain tumor surgery is not painful. Post-treatment rehabilitation helps manage any discomfort.
Previous blog

What Is The Most Common Cause Of Blood In Urine?
Next blog