Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: What You Need To Know
Category: Rheumatology
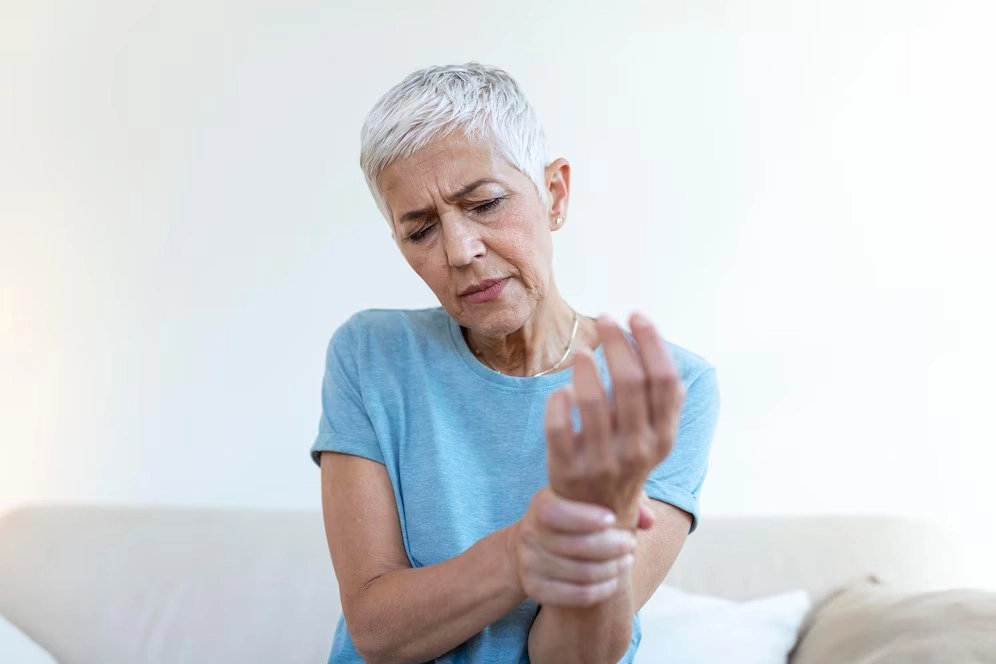
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system targets the synovium - the lining of membranes surrounding the joints. This results in inflammation, which can lead to joint damage and chronic pain. While Rheumatoid Arthritis commonly affects joints in the hands, wrists, and knees, it can also impact other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, lungs, and blood vessels.
Rheumatoid Arthritis a progressive disease, meaning its symptoms worsen over time. Early detection and treatment are crucial to manage the condition effectively and prevent severe complications.
Symptoms Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis can vary in severity and may develop gradually or appear suddenly. Some common signs include:
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Swelling: Joints may appear red, warm, and swollen due to inflammation.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that can interfere with daily activities.
- Fever: Low-grade fevers may accompany joint pain.
- Loss of Joint Function: Difficulty performing everyday tasks like gripping or bending.
- Symmetry of Symptoms: Both sides of the body are often affected equally.
- Rheumatoid Nodules: Firm lumps under the skin near affected joints.
Causes Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
While the exact cause of Rheumatoid Arthritis is unknown, several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetics: A family history of Rheumatoid Arthritis increases the risk due to inherited genes affecting immune function.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain viruses or bacteria may trigger an autoimmune response in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Hormonal Factors: Rheumatoid Arthritis is more common in women, suggesting hormonal influence.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is strongly linked to the onset and progression of RA.
- Obesity: Excess weight can exacerbate joint strain and inflammation.
Diagnosis Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis involves a combination of medical history, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests. Key steps include:
- Physical Exam: Checking for joint swelling, tenderness, and range of motion.
- Blood Tests: Measuring markers like rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies, and inflammation levels through ESR or CRP.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds to assess joint damage and inflammation.
Early diagnosis is critical for initiating treatment and preventing irreversible joint damage.
Treatment Options For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment focuses on controlling inflammation, relieving symptoms, and preventing joint damage. A comprehensive treatment plan may include:
1. Medications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Slow disease progression and prevent joint damage.
Biologic Agents: Target specific immune system components involved in inflammation.
Corticosteroids: Quickly reduce inflammation and pain during flare-ups.
2. Physical Therapy
Exercise and therapy improve joint flexibility, strength, and overall function. A physical therapist can design a program tailored to your needs.
3. Surgery
In severe cases, surgical options like joint replacement or tendon repair may be necessary to restore mobility and reduce pain.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage symptoms effectively.
Lifestyle Tips For Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis requires a proactive approach to improve quality of life. Consider these strategies:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like swimming, yoga, or walking to maintain joint mobility.
- Balanced Diet: Include anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, fruits, and vegetables. Avoid processed and sugary foods.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
- Stress Reduction: Practice mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Adequate Rest: Ensure proper sleep to combat fatigue and promote recovery.
- Joint Protection: Use assistive devices and avoid repetitive stress on affected joints.
How Rheumatoid Arthritis Differs From Other Forms Of Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis is often confused with osteoarthritis, but the two differ significantly:
- Cause: RA is autoimmune, while osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear.
- Affected Joints: RA often affects smaller joints symmetrically, while osteoarthritis targets weight-bearing joints.
- Symptoms: RA includes systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever, unlike osteoarthritis.
Complications Of Rheumatoid Arthritis
If left untreated, Rheumatoid Arthritis can lead to:
- Joint Deformity: Permanent damage and misalignment of joints.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Lung Problems: Inflammation in the lungs causing shortness of breath.
- Osteoporosis: Weak bones due to inflammation and steroid use.
- Infections: Weakened immune system from RA or its treatments.
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospital For Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment?
At Lokmanya Hospital, we offer a comprehensive approach to managing rheumatoid arthritis, combining cutting-edge technology with personalized care. Our team of expert rheumatologists and orthopedic surgeons brings extensive experience in RA treatment. We provide state-of-the-art diagnostic tools for early and accurate detection, along with a holistic care plan that includes physical therapy, diet counseling, and psychological support. Our patient-centered approach ensures that we create tailored treatment plans to suit each individual's needs, ensuring optimal outcomes.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a challenging condition, but with early diagnosis, effective treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, it can be managed successfully. If you're experiencing symptoms or have concerns about joint health, consult a healthcare provider promptly. Lokmanya Hospital’s dedicated team is here to help you regain control over your life and improve your overall well-being.
FAQs
1. Can rheumatoid arthritis be cured?
While there is no cure, effective treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
2. What is the best diet for RA?
An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is beneficial.
3. Are there natural remedies for RA?
While natural remedies like turmeric and fish oil may help reduce inflammation, consult your doctor before use.
4. How long does it take for RA symptoms to improve with treatment?
Improvement varies but is typically seen within weeks to months after starting treatment.
5. Is surgery common for RA?
Surgery is usually a last resort for severe cases when other treatments fail.