Is Jaggery Good For Diabetes?
Category: Blogs
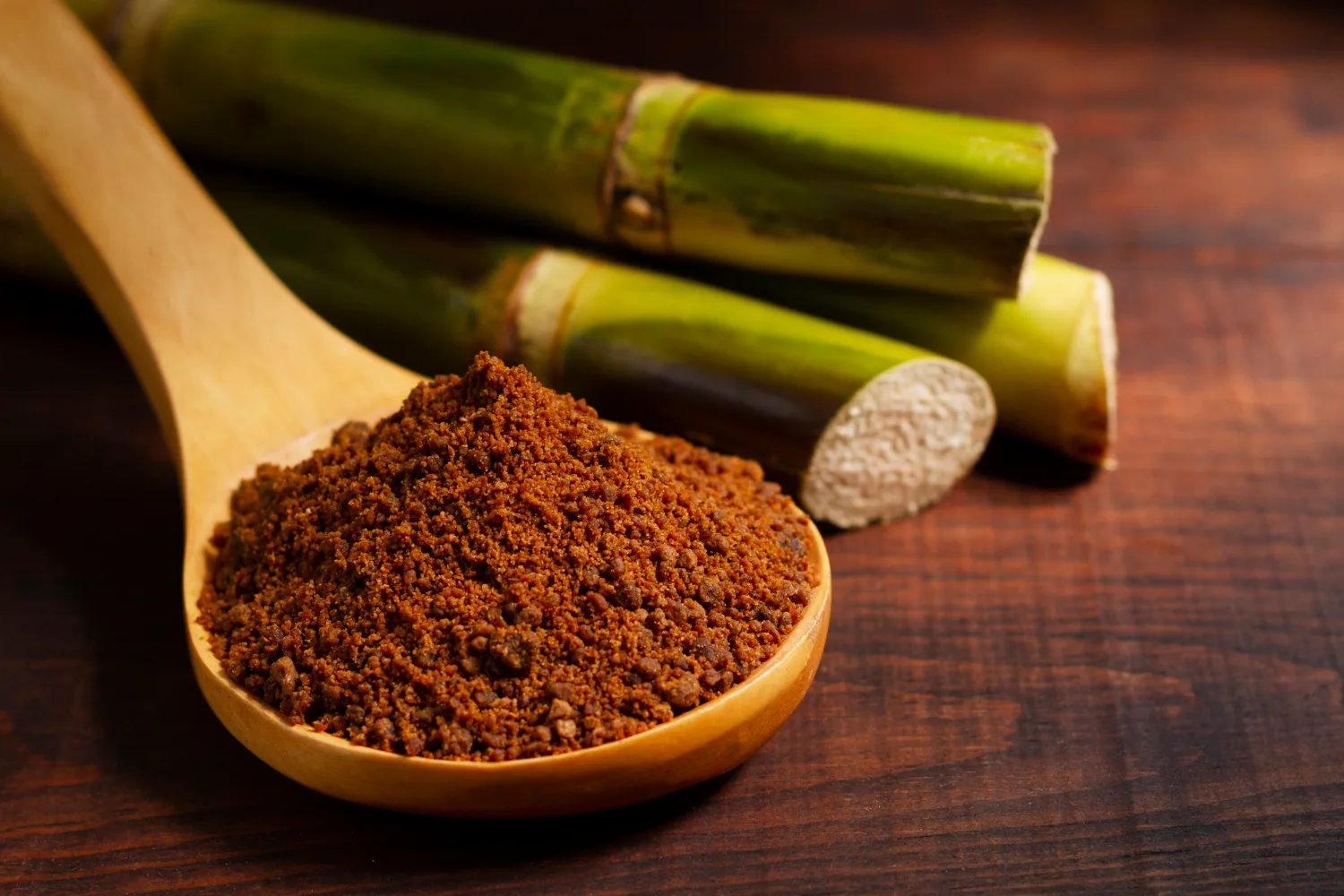
Jaggery, a traditional unrefined sweetener made from sugarcane or palm sap, is widely used in many cultures as a healthier alternative to refined sugar. Known for its rich mineral content and earthy flavor, jaggery is often touted as a natural, nutritious sweetener. But when it comes to diabetes, one of the most common chronic health conditions worldwide, many wonder: Is jaggery good for diabetes?
At Lokmanya Hospitals, recognized as one of the best hospitals for diabetes treatment in Pune, we understand how important it is for diabetes patients to make informed dietary choices. Managing blood sugar is critical in diabetes care, and every element of your diet plays a role in controlling your condition effectively. This blog aims to answer your most searched questions — What is jaggery? Why is it popular? When can it be consumed safely by diabetics? — and guide you with expert advice.
What Is Jaggery and How Is It Different From Sugar?
Jaggery is a traditional sweetener made by boiling raw sugarcane juice or palm sap until it solidifies. Unlike refined white sugar, jaggery retains some molasses, which contains trace amounts of minerals like iron, magnesium, potassium, and antioxidants. This makes it seem like a healthier option at first glance.
However, despite these benefits, jaggery is still a form of sugar, consisting mainly of sucrose, which the body breaks down into glucose, potentially affecting blood sugar levels.
Why Is Jaggery Considered a Better Option Than Refined Sugar?
- Nutritional Content: Jaggery contains small amounts of vitamins and minerals, which are stripped away during the refining process of white sugar.
- No Chemical Additives: Unlike processed sugar, jaggery is usually free from chemical bleaching agents.
- Lower Glycemic Index (GI): Jaggery reportedly has a slightly lower GI than white sugar, which means it may cause a slower rise in blood glucose levels.
Is Jaggery Good for Diabetes? What Does Science Say?
For people with diabetes, managing blood glucose levels is the top priority. Jaggery, although more natural than refined sugar, still consists mainly of carbohydrates that convert into glucose in the body. Therefore, consuming jaggery in large quantities can spike blood sugar levels.
Key Points:
- Jaggery is not sugar-free: It contains sucrose, which impacts blood glucose.
- Moderation is crucial: Small amounts may be acceptable, but excess consumption can be harmful.
- Individual response varies: Some diabetics may tolerate small amounts without significant blood sugar spikes, while others may not.
What Are the Health Benefits of Jaggery?
Despite its risks for diabetics, jaggery offers some benefits:
- Rich in iron: Helps prevent anemia.
- Contains antioxidants: Which can combat oxidative stress.
- Aids digestion: Traditionally used to improve digestion and detoxify the liver.
These benefits, however, do not negate the need for caution in diabetic patients.
What Are the Alternatives to Jaggery for Diabetics?
For those managing diabetes, safer sweetening options include:
- Stevia: A natural sweetener with zero calories.
- Erythritol: A sugar alcohol with minimal impact on blood sugar.
- Monk fruit sweetener: Natural and low GI.
Choosing these alternatives can help satisfy sweet cravings without compromising blood sugar control.
How Can You Incorporate Jaggery in Your Diet If You Have Diabetes?
If you want to enjoy jaggery, follow these tips:
- Consult your doctor or dietitian: Before including jaggery in your diet.
- Keep portions very small: A tiny piece occasionally is better than regular consumption.
- Pair with fiber-rich foods: This slows sugar absorption.
- Monitor blood sugar regularly: To assess your body's response.
Why Choose Lokmanya Hospitals for Diabetes Care?
Managing diabetes requires expert care, personalized plans, and continuous monitoring. Lokmanya Hospitals, widely recognized as the best hospital for diabetes treatment in Pune, offers cutting-edge diagnostics and compassionate care tailored to each patient’s needs. Our experienced endocrinologists and dietitians guide you through safe dietary choices — including the use of natural sweeteners like jaggery — and design treatment plans that suit your lifestyle.
Lokmanya’s Approach to Diabetes Management
At Lokmanya Hospitals, we go beyond routine diabetes care—we empower you to take charge of your health. With advanced glucose monitoring, expert diagnostics, and personalized nutritional counseling, our approach focuses on sustainable lifestyle changes, including safe sweetener options and balanced diet plans.
Our holistic programs also address diabetes-related complications, offering access to top-tier services and comprehensive care. When you choose Lokmanya Hospital, you’re choosing a trusted healthcare partner committed to long-term wellness and compassionate support at every step.
Conclusion
So, is jaggery good for diabetes? The answer is nuanced. While jaggery contains more nutrients than refined sugar, it is still a sugar source that can raise blood glucose levels. For diabetics, moderation is essential, and jaggery should be consumed cautiously and under medical advice.
If you have diabetes and are unsure about including jaggery or other sweeteners in your diet, visit Lokmanya Hospitals, the best hospital for diabetes treatment. Our experts will help create a safe, effective, and sustainable plan tailored to your health needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why do diabetics need to be cautious with jaggery?
Jaggery raises blood sugar just like any other sugar source. People with diabetes have impaired glucose metabolism, so controlling intake is essential to avoid complications. - What is the glycemic index (GI) of jaggery?
The GI of jaggery is moderately high, ranging approximately between 50 and 70, depending on the source. This means it can raise blood sugar moderately quickly. - Can jaggery replace artificial sweeteners in diabetic diets?
While jaggery is natural, artificial sweeteners have zero or very low calories and do not raise blood glucose. Jaggery can be used sparingly but should not be a substitute for healthier sugar alternatives in strict diabetic diets. - When is it safe to consume jaggery if you have diabetes?
Occasional, very limited consumption combined with careful blood sugar monitoring and an overall balanced diet may be safe, but always under medical guidance.

Previous blog